Certain Authorities Having Jurisdiction (AHJs) have recently implemented changes to permit regulations for battery installation in garages.
All projects with batteries in the garage are now required to show a garage layout plan in the permit plan set.
Solargraf has implemented the changes in its AHJ database incorporating batteries in the garage for PV permit design automation with the criteria as show below:
- Criteria for placing Energy Storage System (ESS) in subject to damage area of the garage plan.
- Criteria for placing ESS in not subject to damage area of the garage plan.
AHJs that require a garage plan are:
- LA county (also requires fire sprinklers)
- Oxnard
- Rocklin
- Santee
- Marin County
- Oceanside
- Camarillo
- Chula Vista
- Bakersfield
- Temecula
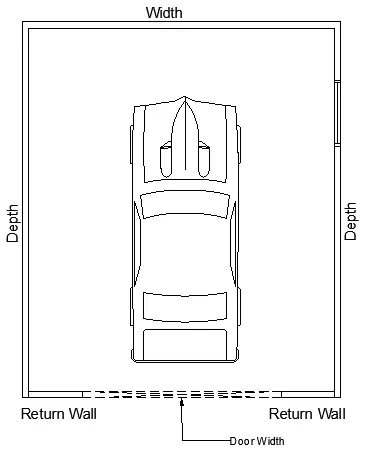
Input requirement from installer for an initial garage plan layout:
- Width of garage
- Depth of garage
- Door width
- Return wall width if available.
- Position of the return wall- left/right/both
Garage Layout:
Minimum Standard Garage Dimensions (feet) at a glance:
| One-Car garage size (WxD) | Two-Car garage size (WxD) | Three-Car garage size (WxD) |
|---|---|---|
| 12'x20' | 20'x20' | 26'x20' |
The standard size for a single vehicle garage door is a minimum of 9 feet.
Rule and requirement of battery garage layout plan as IFC section 1207.11.3:
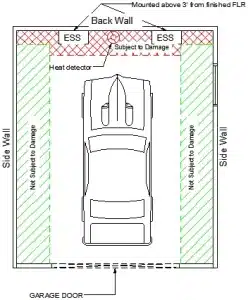
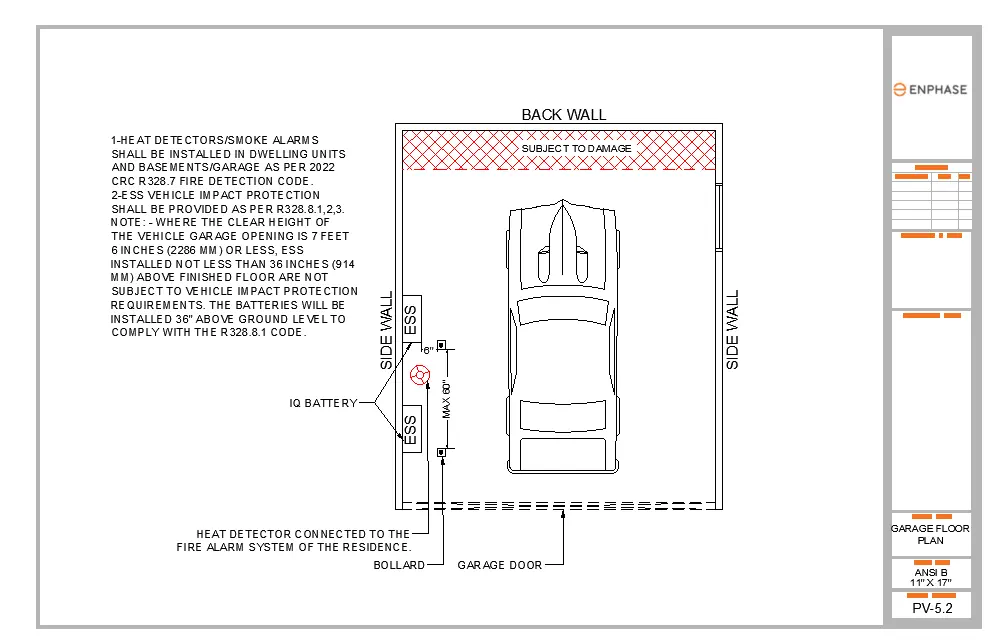
Where an ESS is installed in the normal driving path of a vehicle within the garage, impact protection with IFC section 1207.11.3 shall be provided. The normal driving path is a space between the garage vehicle opening and the interior face of the back wall to a height of 48 inches (1219 mm) above the finished floor. The width of the normal driving path shall be equal to the width of the garage door opening. Impact protection shall also be provided for an ESS installed at either of the following locations (see Figure 1207.11.7.1).
- On the interior face of the back wall and located within 36 inches (914 mm) to the left or right of the normal driving path.
- On the interior face of the side wall and located within 24 inches (610 mm) of the back wall and 36 inches (914 mm) of the normal driving path.
Exception: Where the clear height of the vehicle garage is 7 feet 6 inches or less, an ESS installed not less than 36 inches (914 mm) above the finished floor are not subject to vehicle impact protection requirements.
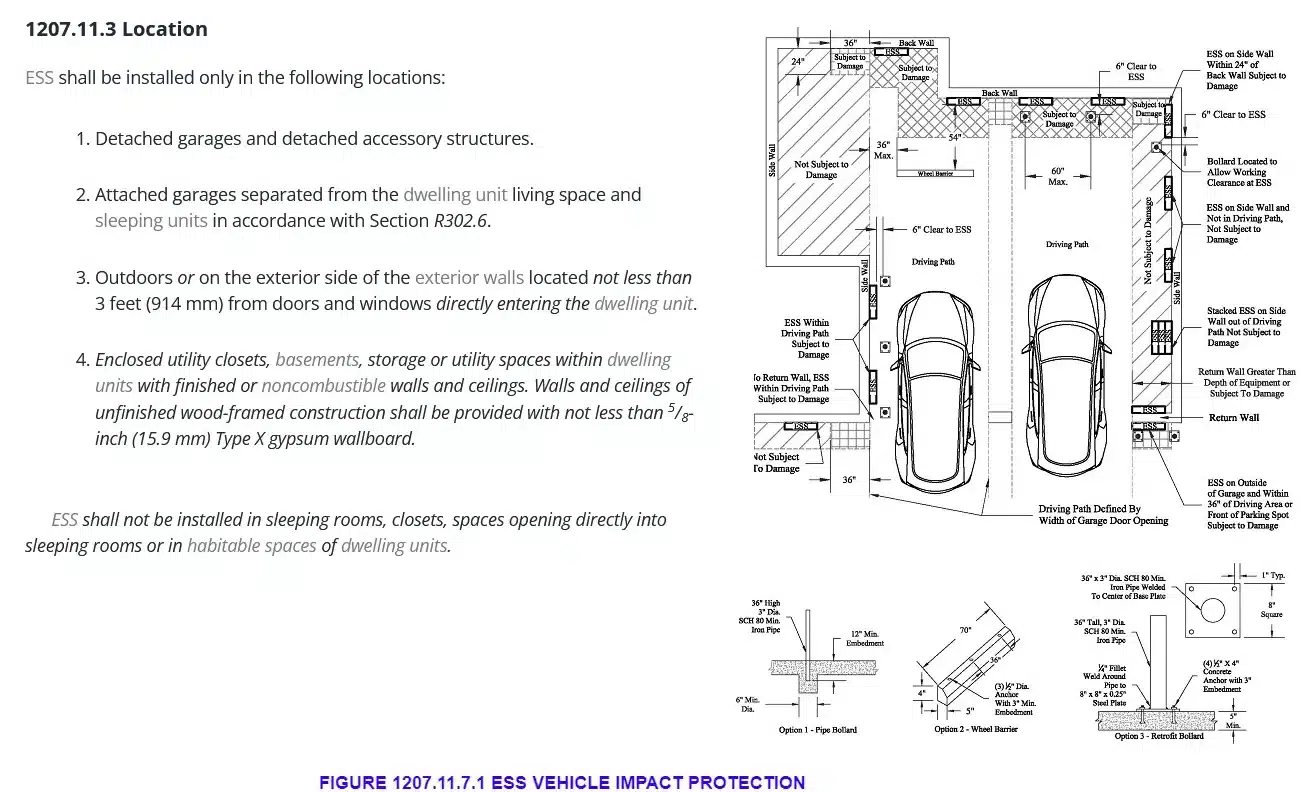
 Red → ESS > 36 inches height = No Bollard
Red → ESS > 36 inches height = No Bollard
Red → ESS < 36 inches height = Bollard
Red → ESS < 36 inches height + wheel barrier = No Bollard
Green → ESS < 36 inches height = No bollard
Note: Wheel barrier to be placed a minimum 54 inches from the battery installed on the back wall.
ESS location scenario matrix:
| ESS Location | ESS mounting height from finished floor | Impact protection required? | Reference figure |
|---|---|---|---|
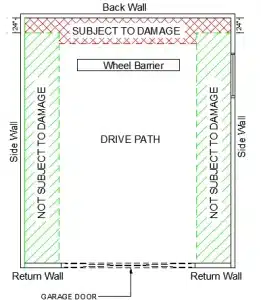
| Scenario I: Side/ back wall | > 36 inches | No | Fig: a |
| Scenario II: Side wall/return/ back wall | < 36 inches | No | Fig: b |
| Scenario III: On the wall within the drive path | < 36 inches | Yes (*) | Fig: c |
Note: (*) Bollards with a minimum 6 inch clearance from the battery and the maximum gap between two bollards should be 60 inches.
Scenario I: ESS are installed above 36 inches from the finished floor of the garage. Here in this case the bollards are not required because the ESS are mounted above the “subject to damage area” of the garage layout.
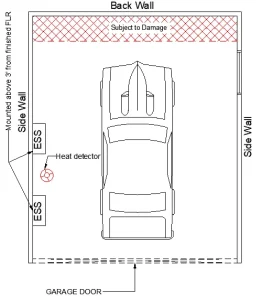
Fig a: Scenario 1: Side/Back Wall
Scenario III: ESS are installed within 36 inches from the finished floor and placed in the drive path/subject to damage area of the garage. Here in this case bollards are required for impact protection with a minimum 6 inch clearance from the ESS front edge/face and a recommended maximum distance of 60 inches between bollards.
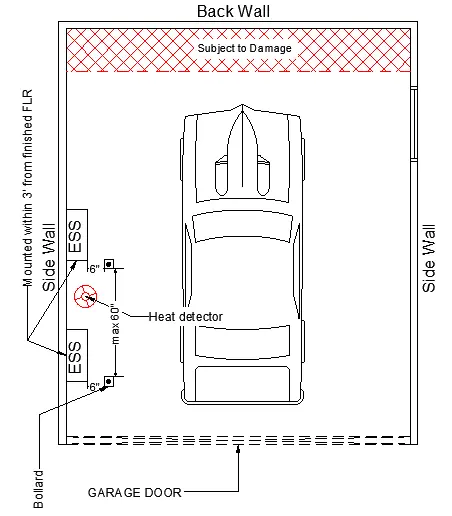
Fig c: Scenario III: On the wall within the drive path
Additional requirements:
All batteries installed inside the garage are required to provide a heat detector in compliance with the IFC code.
Heat alarm and smoke detectors requirement:
Applicable codes:
- 2021 International Fire Code 1207.11.6
- 2021 International Residential Code R328.7 & R104.10
- 2022 California Fire Code 1207.11.6
- 2022 California Residential Code R328.7 & R104.10
- 2020 NFPA 855 15.9
- 2023 NFPA 855 15.7
Applicable standards:
- UL 268 – UL Standard for Smoke Detectors for Fire Alarm Signaling Systems
- UL 521 – UL Standard for Safety for Heat Detectors for Fire Protective Signaling Systems
- UL 539 – UL Standard for Safety for Single and Multiple Station Heat Alarms (residential heat alarms)
- UL 985 – UL Standard for Household Fire Warning System Units
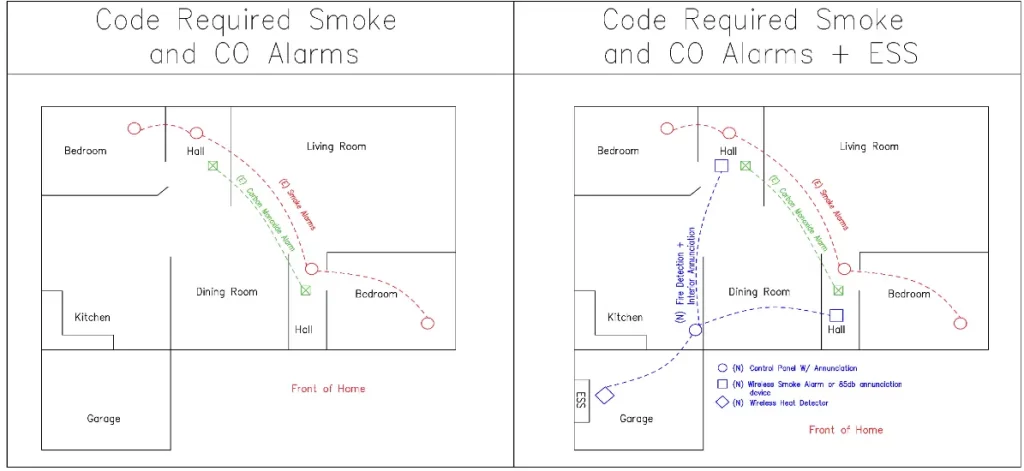
Figure 1 (above): code required smoke and carbon monoxide detector placement and placement of fire alarm equipment for installation of ESS in unconditioned space.
Install a heat alarm detector on the wall or ceiling in the garage near the battery location. The heat detector should be UL 539 listed and approved by the local authority (AHJ). The heat detector in the garage shall be connected to the existing fire alarm system of the residence. This integration to the fire alarm system shall enable detection of any heat in the garage which will alert alarms placed in the habitable spaces of a house/residence.
Expected output with bollard:
Expected output without bollard:
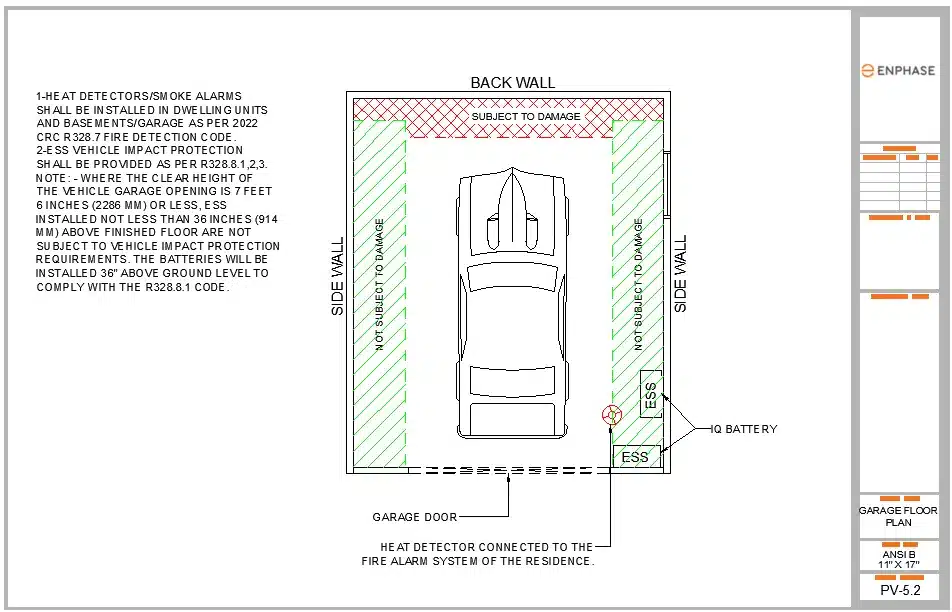
Here are some of the examples of how permit plan sets with battery in garage are created on Solargraf as per the new changes.
Sample 1: Batteries are placed on the right-side wall with minimum clearance. Bollards are not required here because of the return wall natural clearance of 36 inches from interior wall. The heat detector was placed nearby the battery location.
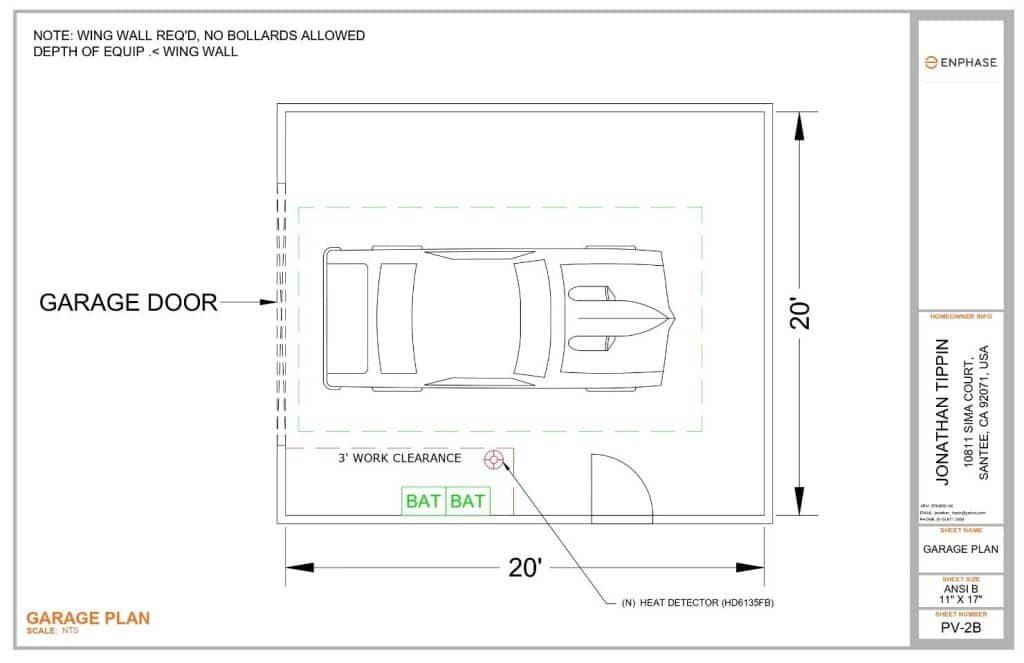
Sample 2: Two vehicles in single garage. Batteries are placed on the left-side wall with minimum clearance. Bollards are not required here because of the return wall natural clearance of 36 inches from interior wall. The heat detector was placed nearby the battery location.
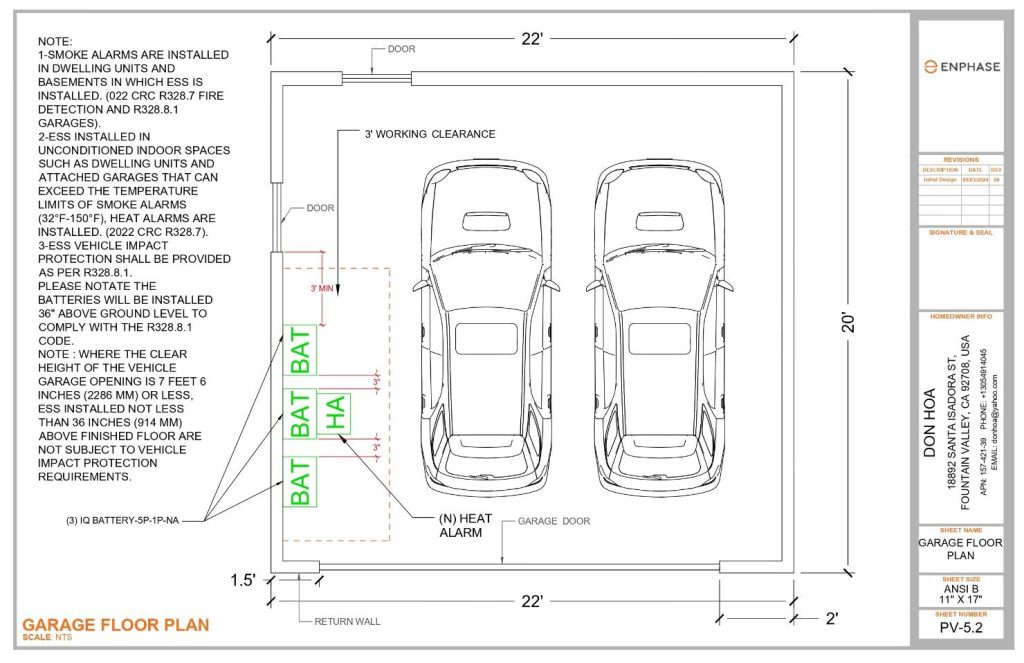
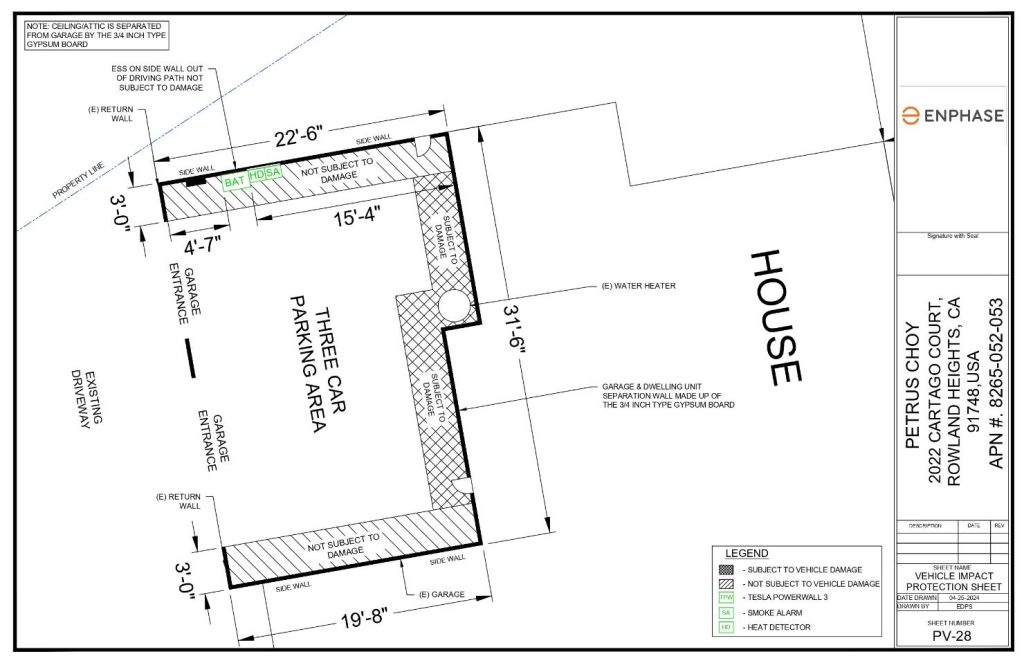
Sample 3: Batteries were placed on the left-side wall of the non-uniform garage plan by maintaining minimum clearance. The garage has multiple entrance gates and the subject clearance and not subject to clearance are well defined in the plan.
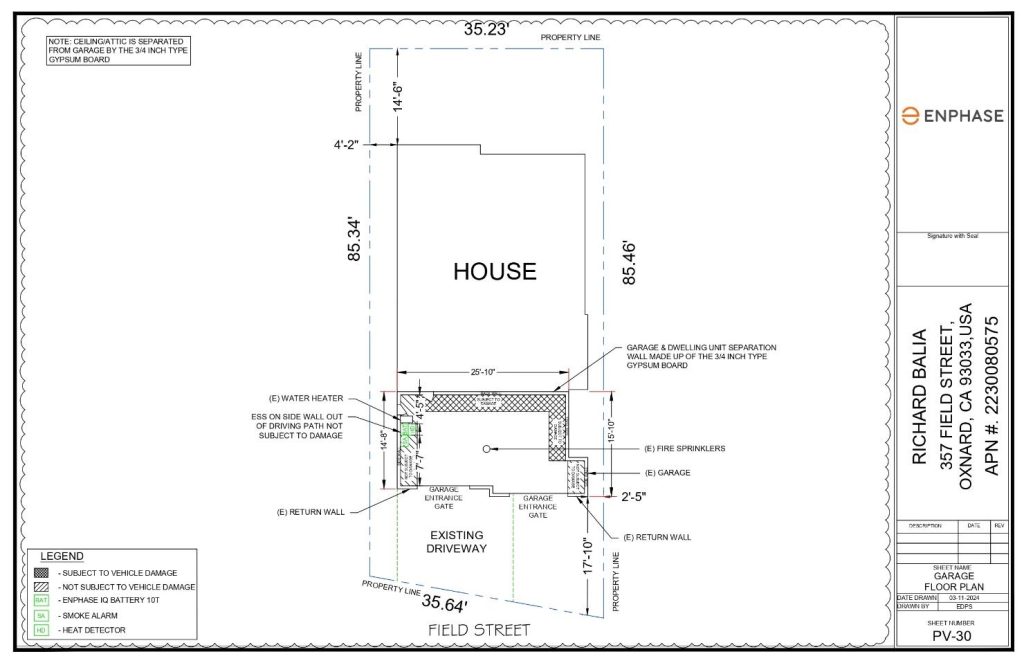
Sample 4: This is a three vehicles compatible garage with two entry points. The battery was on the left side of the interior with natural return clearance.
Solargraf’s AHJ database is updated with all the latest changes related to battery permits. Stay on top of the regulations effortlessly, ensuring smooth permit processes and streamlined compliance for your solar projects. Experience peace of mind with Solargraf knowing your designs are up-to-date with industry standards.
Schedule a demo to learn more about the latest changes.
Thank you for your interest in this article. In order to better serve our clients we ask that you fill out a simple form in order to access this premium content.


 United States
United States Germany/Austria
Germany/Austria Brazil
Brazil Netherlands
Netherlands